Free Download Programming in JAVA Notes in pdf – Bca 2nd Semester. High quality, well-structured and Standard Notes that are easy to remember.
Welcome to Bcanpm.com
Bcanpm provides standard or well-structured Bca Notes for students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bca are available on www.bcanpm.com. In this post you can download notes of Programming in JAVA Notes (C3). All units are available to download for free.
Programming in JAVA Notes Unit 1 – 5
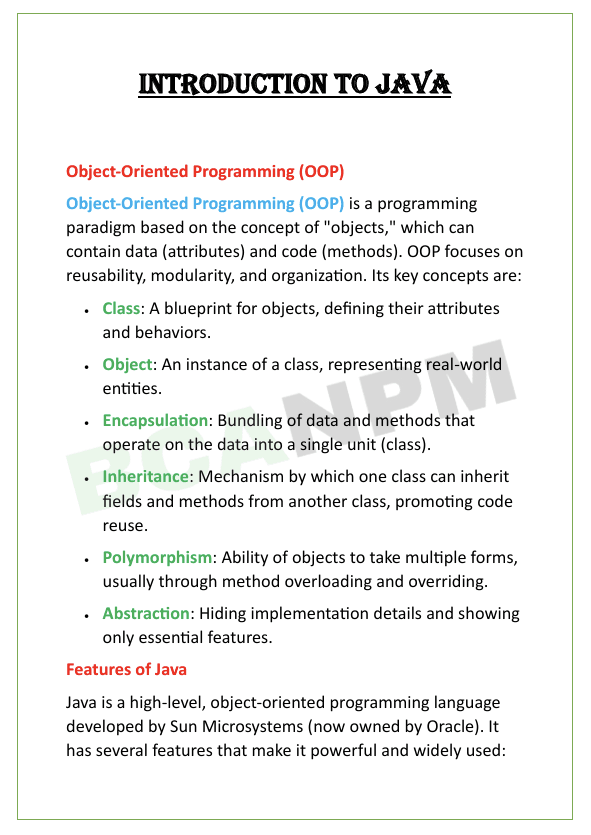
Unit 1: Introduction to java
“Java” is a high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995. It is designed to be platform-independent.

Unit 2: Java Programming
“Java” follows the “write once, run anywhere” (WORA) philosophy, making it versatile for a variety of applications, from desktop software to mobile apps and enterprise-level systems.

Unit 3: AWT and Event Handling
“AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)” is Java’s platform-dependent API for building graphical user interfaces (GUIs), providing components like windows, buttons and text fields.
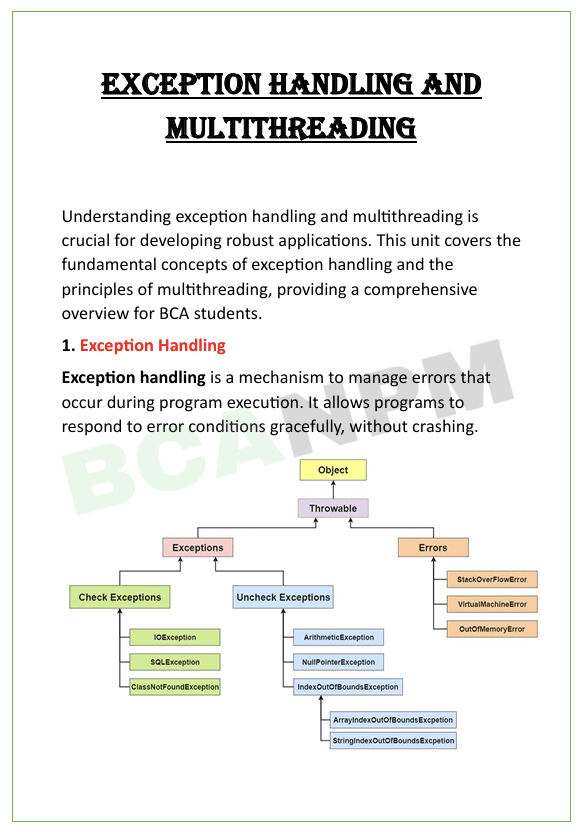
Unit 4: Exception Handling and Multithreading
“Exception Handling” in Java is a mechanism for managing runtime errors, ensuring that normal program flow can be maintained even when exceptions occur.
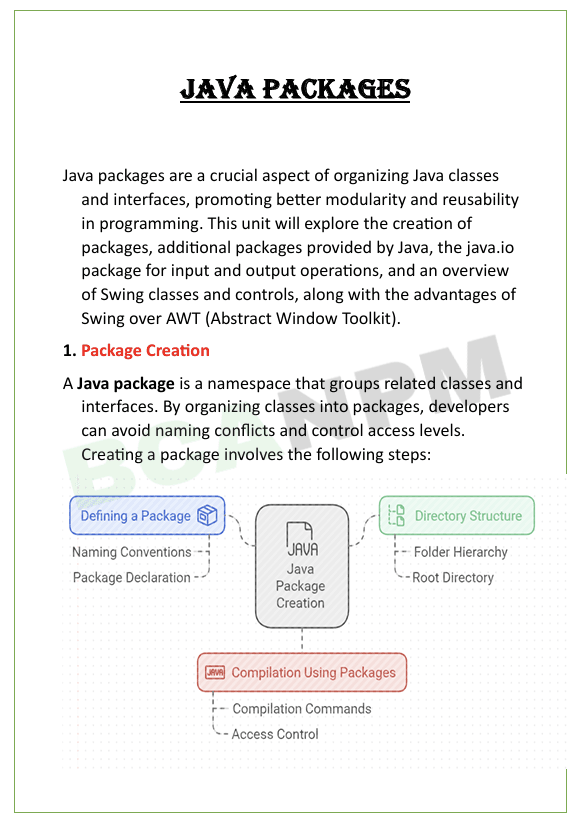
Unit 5: Java packages
“Java packages” are a way to organize and group related classes and interfaces, providing modularity and structure to large programs.
Syllabus of Programming Fundamentals using C/C++
UNIT – 1
(a) Introduction to Java Programming:
History and features of Java
Java platform and Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
Basic structure of a Java program
Compiling and running Java programs
Data types, variables, constants, operators, and expressions
(b) Control Statements:
Decision-making – if, if-else, switch
Looping – for, while, do-while
Jump statements – break, continue, return
UNIT – 2
Classes and Objects:
Defining a class and creating objects
Constructors – default, parameterized, and copy constructors
Overloading methods and constructorsthis keyword
Static members – variables and methods
UNIT – 3
Inheritance and Polymorphism:
Inheritance – single, multilevel, hierarchicalsuper keyword
Method overriding
Dynamic method dispatch
Final keyword, abstract classes, and methods
Introduction to interfaces and implementation
UNIT – 4
Packages, Exception Handling, and Strings:
Java packages – built-in and user-defined packages
Importing packages
Exception handling – try, catch, throw, throws, finally
Built-in exceptions and creating user-defined exceptions
String class and string buffer – string operations and methods
UNIT – 5
Applets and File Handling:
Java Applets – lifecycle, Applet class, methods, and simple applet programs
Graphics in applets – drawing shapes, colors, fonts
File handling in Java – FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, FileReader, FileWriter
Reading and writing files
Serialization (basic concept)