
Free Download Information Security Notes in pdf – Bca 5th Semester. High quality, well-structured and Standard Notes that are easy to remember.
Welcome to Bcanpm.com
Bcanpm provides standard or well-structured Bca Notes for students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bca are available on www.bcanpm.com. In this post you can download Information Security Notes (DSE1). All units are available to download for free.
Information Security Notes Unit 1 – 10
Unit 1: Introduction to Information Security
“Introduction to Information Security” focuses on protecting information and systems from unauthorized access, misuse, disruption or destruction.

Unit 2: Cryptography and Encryption Techniques
“Cryptography and Encryption Techniques” are essential components of information security, focusing on securing data through mathematical algorithms.

Unit 3: Network Security
“Network Security” involves protecting computer networks from unauthorized access, misuse, and cyber threats to ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data.

Unit 4: Security in Operating Systems and Databases
“Security in Operating Systems and Databases” focuses on protecting the core components of computing systems from unauthorized access, breaches and vulnerabilities.

Unit 5: Risk Management and Security Policies
“Risk Management and Security Policies” are critical aspects of ensuring organizational information security.
Syllabus of Information Security
Unit 1: Introduction to Information Security
Definition and Scope
- What is Information Security?
- Importance of information security.
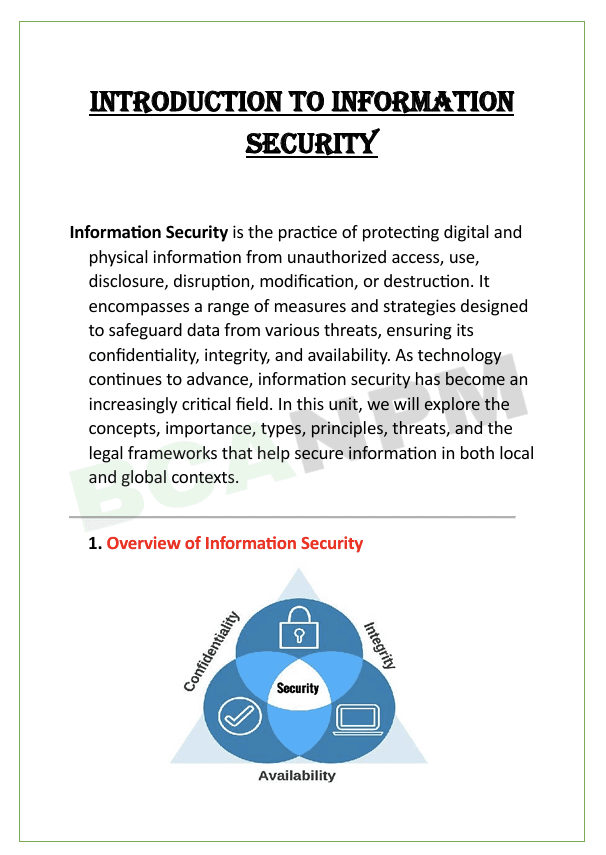
- Goals of information security: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA triad).
Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Types of threats: malware, phishing, social engineering, etc.
- Common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs).
- Risk assessment and management.
Unit 2: Cryptography
Introduction to Cryptography
- Definition and importance.
- Historical background: classical cryptography (Caesar cipher, Vigenère cipher).
Symmetric Key Cryptography
- Block ciphers and stream ciphers.
- DES (Data Encryption Standard), AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
- Key management and distribution.
Asymmetric Key Cryptography
- Public key cryptography principles.
- RSA algorithm, Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
- Digital signatures and certificates.
Unit 3: Network Security
Network Security Basics
- Fundamentals of network security.
- Types of network attacks: DoS/DDoS, man-in-the-middle, packet sniffing.
Network Security Protocols
- Secure communication protocols: SSL/TLS, IPSec.
- Wireless security protocols: WEP, WPA, WPA2.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Types of firewalls: packet filtering, stateful inspection, proxy firewalls.
- IDS and IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems) basics and types.
- Network monitoring and logging.
Unit 4: Operating System Security
Operating System Vulnerabilities
- Common OS vulnerabilities.
- Patch management and updates.
Access Control
- Principles of access control: DAC (Discretionary Access Control), MAC (Mandatory Access Control), RBAC (Role-Based Access Control).
- User authentication methods: passwords, biometrics, multi-factor authentication.
Secure Operating Systems
- Security features in popular operating systems (Windows, Linux, MacOS).
- Hardening techniques and best practices.
Unit 5: Application Security
Web Application Security
- Common web vulnerabilities: SQL injection, XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery).
- Secure coding practices and input validation.
- Web application security tools: OWASP Top 10, web application firewalls (WAF).
Software Development Security
- Secure software development lifecycle (SDLC).
- Static and dynamic analysis tools.
- Code reviews and security testing.
Unit 6: Data Security and Privacy
Data Protection Techniques
- Data encryption at rest and in transit.
- Data masking and tokenization.
- Secure data storage and backup.
Privacy Issues
- Privacy laws and regulations: GDPR, CCPA.
- Privacy-enhancing technologies.
- Data anonymization and pseudonymization.
Unit 7: Cybersecurity Management
Security Policies and Procedures
- Developing and implementing security policies.
- Incident response planning and management.
- Business continuity and disaster recovery planning.
Security Audits and Compliance
- Types of security audits: internal, external, compliance.
- Common compliance frameworks: ISO/IEC 27001, PCI-DSS, HIPAA.
- Audit tools and techniques.
Unit 8: Emerging Trends in Information Security
Cloud Security
- Security challenges in cloud computing.
- Cloud security models and best practices.
- Identity and access management (IAM) in the cloud.
IoT Security
- Security issues in Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- IoT security frameworks and protocols.
- Best practices for securing IoT ecosystems.
AI and Machine Learning in Security
- Role of AI in cybersecurity.
- Machine learning techniques for threat detection and response.
- Challenges and limitations of using AI in security.
Unit 9: Ethical and Legal Aspects of Information Security
Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing
- Principles of ethical hacking.
- Penetration testing methodologies and tools.
- Legal and ethical considerations.
Legal Issues in Cybersecurity
- Cyber laws and regulations.
- Intellectual property rights and digital forensics.
- Case studies on cybersecurity breaches and legal outcomes.
Unit 10: Case Studies and Practical Applications
Real-World Case Studies
- Analysis of major cybersecurity incidents.
- Lessons learned and best practices.
- Impact of cyber-attacks on businesses and society.
Practical Applications
- Hands-on labs and simulations.
- Implementation of security solutions in different environments.
- Capstone project on developing a comprehensive security plan for an organization.