
Free Download Cloud computing Notes in pdf – Bca 5th Semester. High quality, well-structured and Standard Notes that are easy to remember.
Welcome to Bcanpm.com
Bcanpm provides standard or well-structured Bca Notes for students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bca are available on www.bcanpm.com. In this post you can download Cloud computing Notes (DSE2). All units are available to download for free.
Cloud computing Notes Unit 1 – 10

Unit 1: Cloud Architecture and Model
“Cloud Architecture and Models” focus on the framework and service models used to deliver computing resources over the Internet.

Unit 2: Virtualization
“Virtualization” is a technology that allows multiple virtual instances of operating systems, applications or servers to run on a single physical hardware system.

Unit 3: Cloud Infrastructure
“Cloud Infrastructure” refers to the hardware and software components that support cloud computing services.
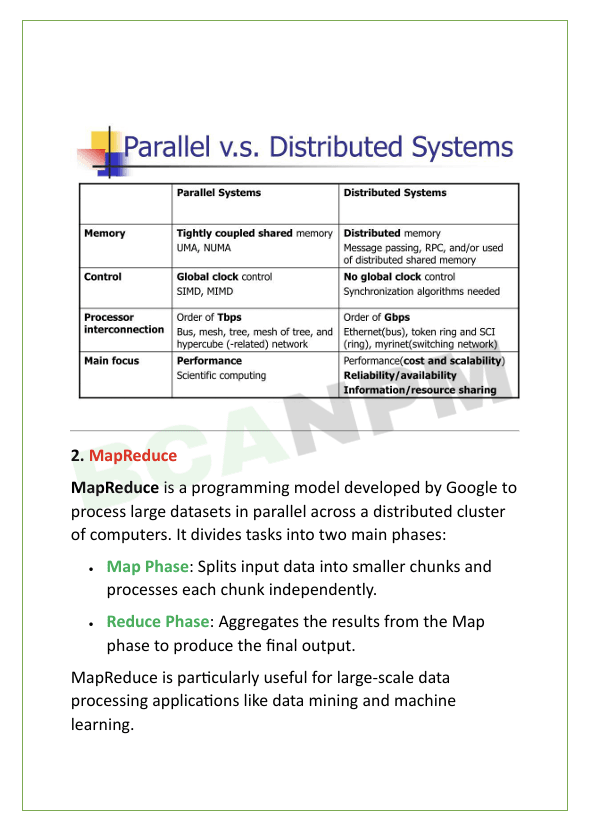
Unit 4: Programming Model
“Programming Models” define the approach and structure for designing and implementing programs in a specific computing environment.

Unit 5: Security in the Cloud
“Security in the Cloud” focuses on protecting data, applications, and infrastructure hosted on cloud platforms from unauthorized access, breaches and cyber threats.
Syllabus of Cloud Computing
Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing
Definition and Characteristics
- What is cloud computing?
- Key characteristics: on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, measured service.
- Benefits and challenges of cloud computing.
Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Historical perspective.
- Comparison with traditional computing models.
- Driving factors behind cloud adoption.
Unit 2: Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Definition and examples.
- Key components: virtual machines, storage, networks.
- Use cases and benefits.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Definition and examples.
- Key components: runtime environment, development tools, databases.
- Use cases and benefits.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Definition and examples.
- Key components: application software, user interface.
- Use cases and benefits.
Unit 3: Cloud Deployment Models
Public Cloud
- Definition and characteristics.
- Advantages and disadvantages.
- Major public cloud providers: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud.
Private Cloud
- Definition and characteristics.
- Advantages and disadvantages.
- Use cases and deployment strategies.
Hybrid Cloud
- Definition and characteristics.
- Advantages and disadvantages.
- Integration and management of hybrid cloud environments.
Community Cloud
- Definition and characteristics.
- Advantages and disadvantages.
- Use cases and deployment strategies.
Unit 4: Cloud Architecture
Components of Cloud Architecture
- Front-end and back-end platforms.
- Cloud-based delivery models.
- Service-oriented architecture (SOA) and microservices.
Virtualization
- Role of virtualization in cloud computing.
- Types of virtualization: server, storage, network.
- Virtualization technologies: hypervisors, containers.
Unit 5: Cloud Storage and Data Management
Cloud Storage
- Types of cloud storage: object storage, block storage, file storage.
- Cloud storage providers: AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage.
- Data redundancy and replication.
Data Management
- Data migration strategies.
- Data backup and recovery.
- Data security and compliance in the cloud.
Unit 6: Cloud Security
Security Challenges in Cloud Computing
- Data breaches, identity theft, account hijacking.
- Shared responsibility model.
Cloud Security Solutions
- Encryption, firewalls, identity and access management (IAM).
- Security as a service (SECAAS).
- Best practices for securing cloud environments.
Unit 7: Cloud Services and Applications
Cloud-Based Services
- Content delivery networks (CDNs).
- Database as a service (DBaaS).
- Big data and analytics in the cloud.
Cloud Applications
- Collaboration tools (e.g., Google Workspace, Microsoft 365).
- Customer relationship management (CRM) systems (e.g., Salesforce).
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle).
Unit 8: Cloud Management and Monitoring
Cloud Management Tools
- Cloud management platforms (CMPs).
- Automation and orchestration tools.
- Cost management and billing.
Monitoring and Performance Management
- Importance of monitoring cloud services.
- Tools for monitoring (e.g., CloudWatch, Azure Monitor).
- Performance tuning and optimization.
Unit 9: Cloud Computing Use Cases
Industry Use Cases
- Healthcare, finance, retail, education.
- Case studies of cloud adoption in various industries.
Emerging Trends
- Edge computing and fog computing.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud integration.
- AI and machine learning in the cloud.
Unit 10: Future of Cloud Computing
Trends and Predictions
- Serverless computing.
- Multi-cloud strategies.
- Quantum computing and its impact on the cloud.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
- Data privacy laws and regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Ethical issues in cloud computing.
- Compliance and governance.